
Session cookies are temporary files that websites store on a user's device while they navigate a site. These cookies are fundamental to the modern web, ensuring key features like maintaining login status or keeping items in the shopping cart—guaranteeing a seamless and uninterrupted browsing experience.
Not all cookies are the same: Session cookies have a unique and important role for both users and businesses, allowing websites to remember visitor information during browsing without storing data long term.
What are session cookies?
A session cookie is a small data file temporarily stored in the visitor’s browser. These cookies enable real-time features that maintain session continuity, such as keeping a user logged in or tracking items in a shopping cart across different pages.
The defining feature of session cookies is their temporary nature: they exist only while the browser is open and are deleted automatically when the browser is closed.
How do session cookies work in practice?
Here’s how session cookies function step by step:
- Session Initialization: When a user visits a website, the server creates a unique session identifier (Session ID) and sends it to the browser as a session cookie.
- Storing the Cookie: The browser stores the session cookie and returns it to the server with every request for the duration of the session.
- Session Management: The server uses the Session ID to connect the user's requests to a temporary session record, which may contain authentication status, preferences, or other session data.
- Session Termination: When browsing ends and the browser is closed, the session cookie is deleted. If the site is visited again later, a new session ID is generated.
What are persistent cookies?
Persistent cookies—also called permanent cookies—remain on the user’s device even after the browser is closed. These cookies have a set expiration date and may last for weeks, months, or even years.
Persistent cookies store information for future visits, such as:
- Saved login credentials.
- User behavior tracking for conversion or marketing analysis.
- Personalization preferences, like language or visual theme settings.
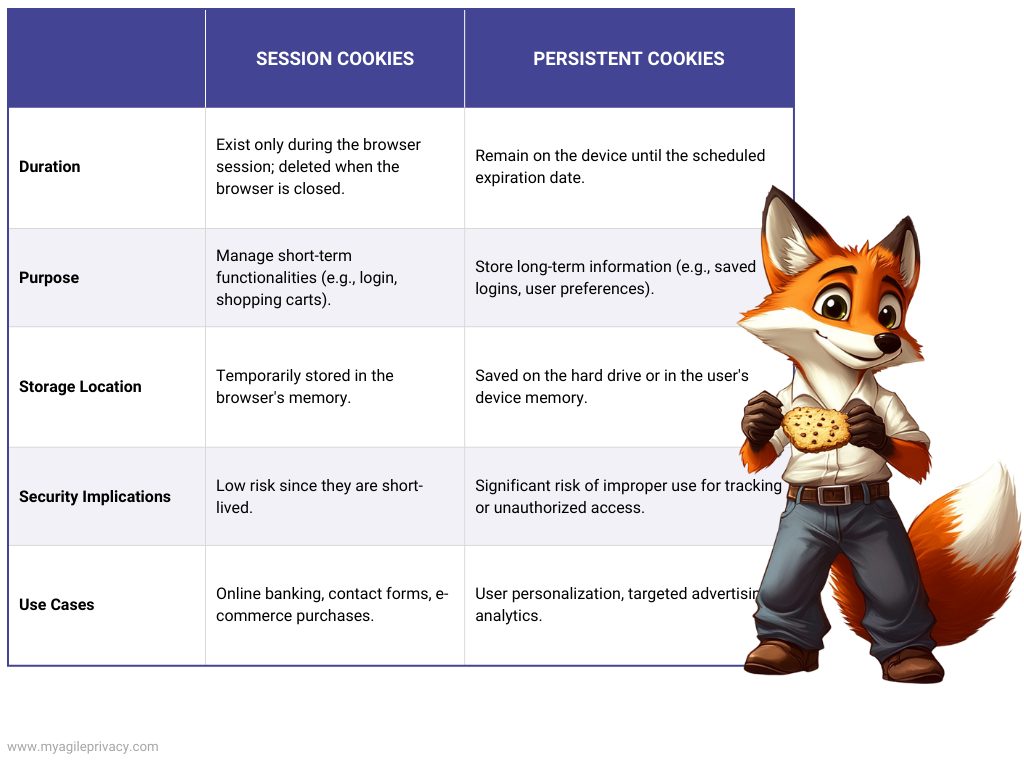
Key differences between session and persistent cookies
Examples of session cookies in action
- E-commerce: Maintain the shopping cart as you browse so checkout works smoothly.
- Online banking: Keep you logged in during a session, with automatic logout after inactivity for security.
- Customer support: Let live chat remain active as you visit different pages.
- Content management systems: Platforms like WordPress use session cookies to keep admin and editing sessions secure.
GDPR and session cookies
The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) governs cookie use, giving users more control over their data. Session cookies are generally categorized as ‘strictly necessary’ for the site to function, so they don’t usually require explicit consent.
Managing consent with My Agile Privacy
To simplify compliance and streamline management, you can rely on innovative tools like My Agile Privacy: a complete, easy-to-use GDPR solution that keeps your compliance automated and effortless.








